往復の滑り接触における摩擦損失の低減に関する研究
理工学部機能創造理工学科 イルマズ エミール 助教
- 研究
【研究の概要】
SDG 7.3 incorporates energy efficiency goals, aiming to double the rate of improvement in global energy efficiency by 2030. In machinery, numerous components exhibit reciprocating motion and often come into contact with each other, generating heat through friction, known as heat loss. By minimizing heat dissipation from these contact surfaces, reciprocating motion can be executed more effectively. Within our laboratory, we are actively researching diverse surface micro-textures designed to mitigate these frictional losses. For this purpose, as an initial step we have designed and constructed a novel experimental setup to quantify frictional forces between two parallel surfaces operating under a hydrodynamic lubrication regime.
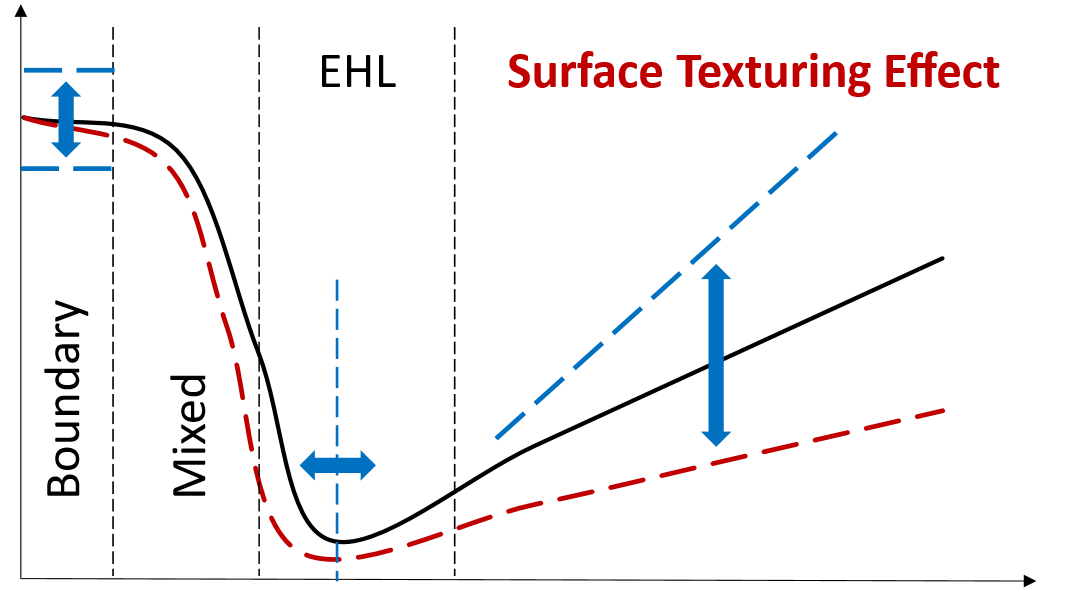
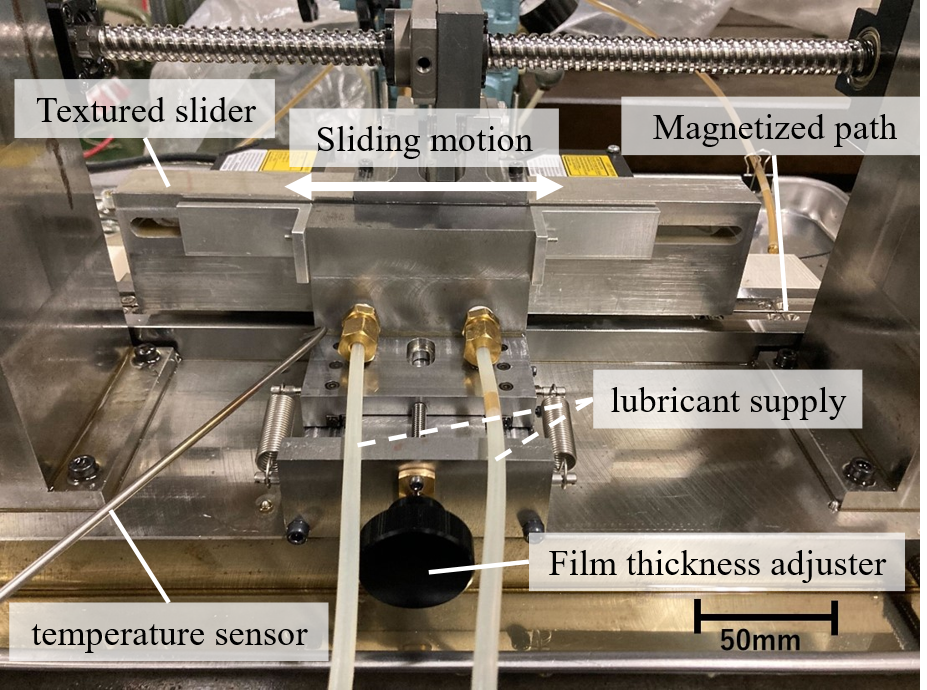
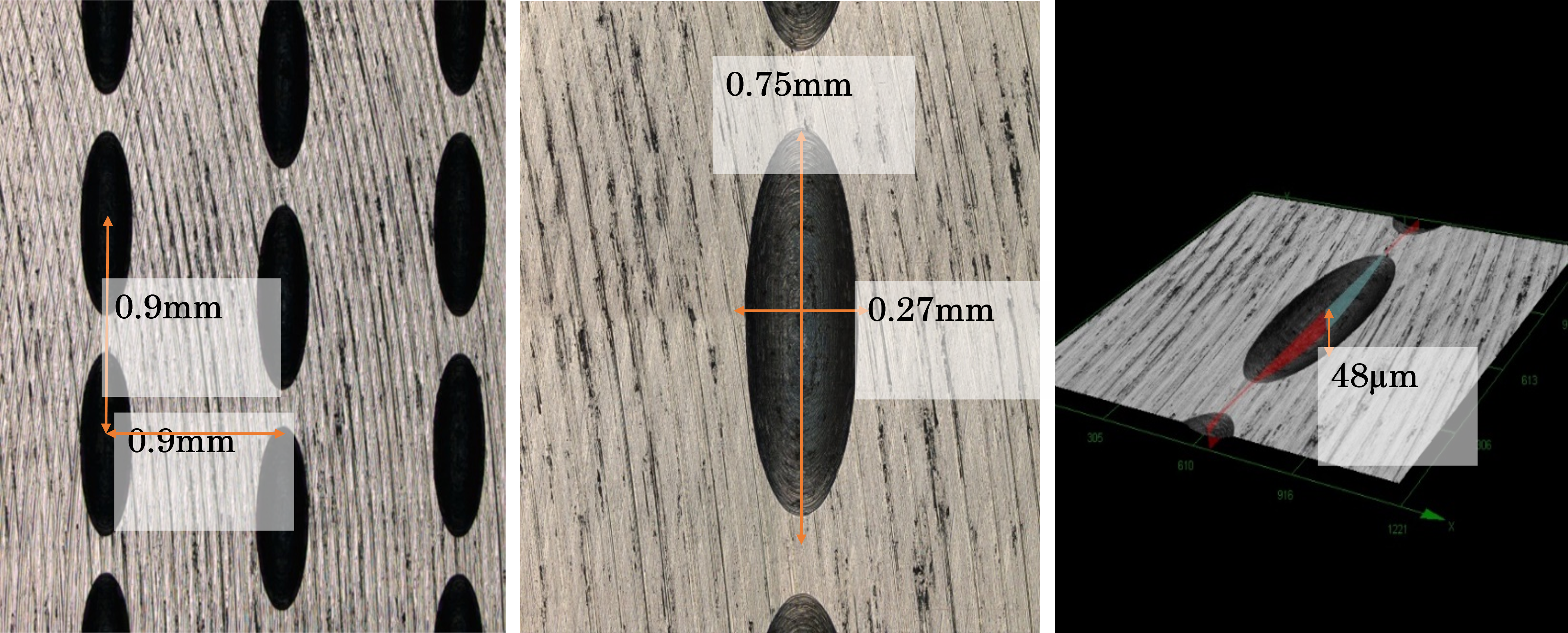
【将来の発展性】
Our objective is to establish a comprehensive set of guidelines for surface micro-texture parameters, such as texture dimensions, orientation, areal density, etc. This initiative is geared towards reducing energy consumption by minimizing frictional losses in reciprocating surfaces. One usage of this technology would be next-generation internal combustion engines (NG-ICEs) as the conventional engines are being adapted to new energy sources such as carbon-free/neutral fuels like hydrogen, ammonia, and e-fuels. Thus, intensive research in power transmission remains crucial for further improvement of these machines. In conventional ICEs, frictional losses constitute approximately 10% of total mechanical losses, with the piston-liner interface alone contributing 50% of these losses. Implementing a well-defined guideline for surface micro-textures holds the potential to elevate overall efficiency, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and increased mileage for NG-ICEs.
