Sado Case
Guangwei Huang, Professor
Graduate School of Global Environmental Studies
- Research
Sado Island is rich in fauna and flora, landscape and culture as well, providing an ideal research field for studying the interactions between nature and humans. In 2022, Sophia University signed a comprehensive partnership agreement with Sado City for collaboration toward the Sado’s sustainability.
Since then, the Institute for Studies of the Global Environment of Sophia University has been conducting various investigations on Sado Island for better understanding its nature and the society. A particular focus is the water environment in Lake Kamo.
Lake Kamo, with approximately 17km of circumferences, is the largest lake in Niigata Prefecture and famous for oyster farming in Japan. In the fall of 2009, this lake experienced its first bloom of the dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama.
However, water quality studies on Lake Kamo are still limited.
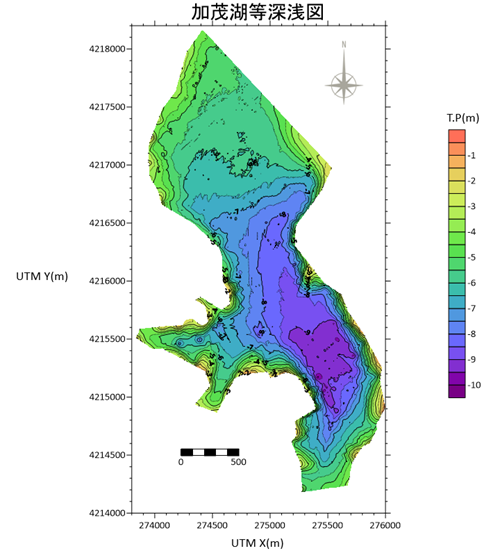
As a first step toward a comprehensive and integrative study of the lake, we conducted a lake morphology survey using ADCP. Figure 1 shows the survey result. Because the last survey was done in 1966, our survey provided new and valuable information regarding the physical attributes of the lake.
Furthermore, water quality survey was conducted in different seasons.
Figure 2 shows the change of TOC (Total Organic Carbon) in the lake from the South to North and the distribution of dissolve oxygen saturation along the lake shore.
Additionally, surveys of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities, and microplastic in Lake Kamo were also carried out in 2023. These outcomes helped us develop further in-depth research plan, which will be implemented in 2024.
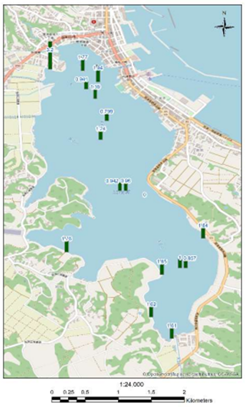
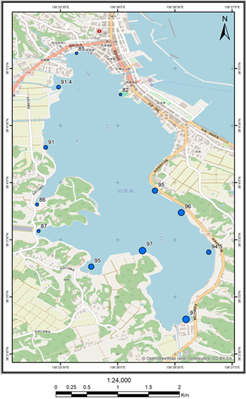
(a)TOC (ppm) in June
(b)DO saturation (%) in December
Fig. 2: Some results of the water quality survey in Lake Kamo



